기반구축사업단 연구 포스터(2025년 한국운동재활학회ㆍ협회 추계학술대회) : 김인홍 연구원 외
페이지 정보

본문
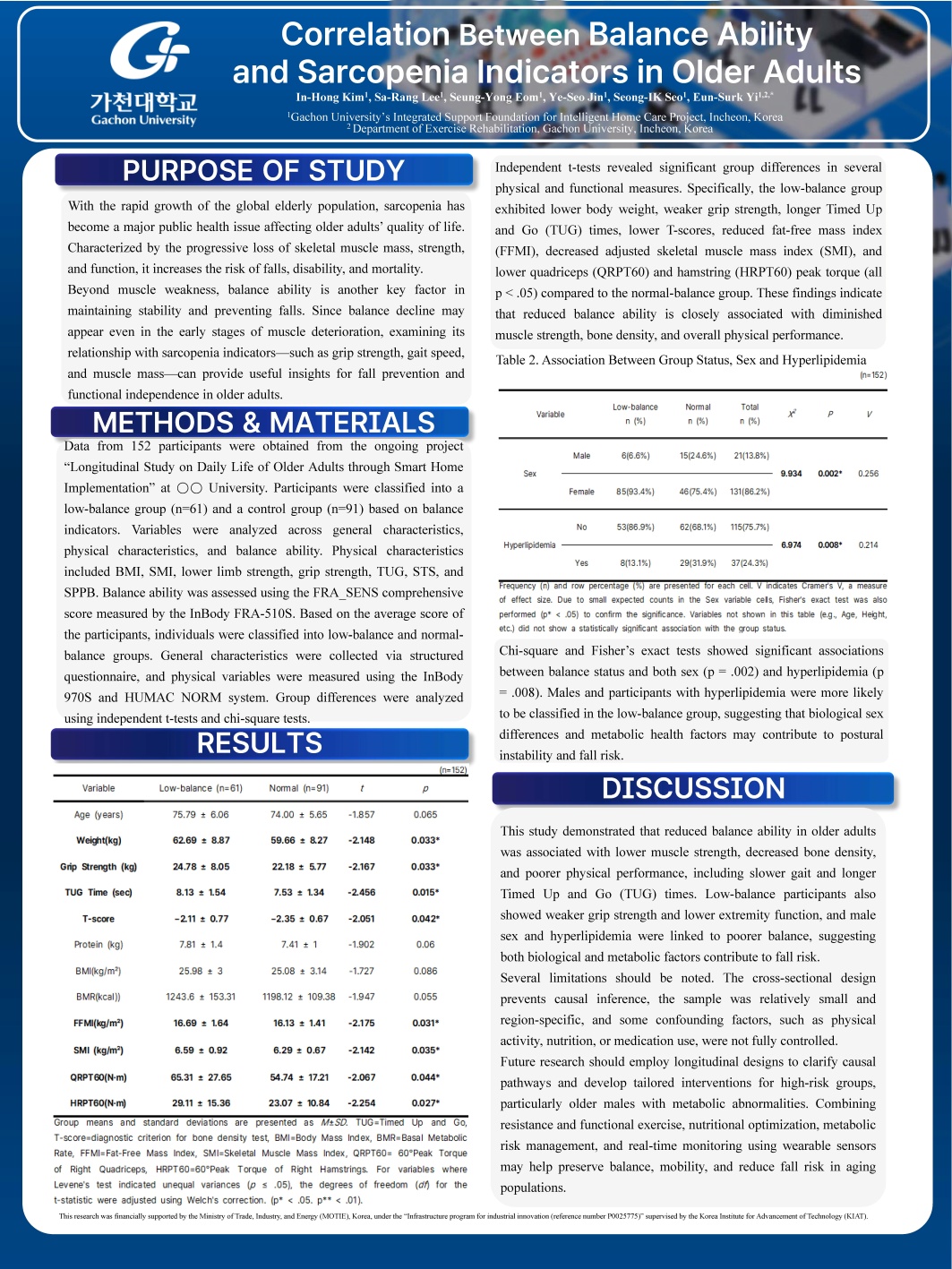
1) 포스터명 : Correlation BetweenBalance Ability and Sarcopenia Indicators in Older Adults
2) 저자 : In-Hong Kim, Sa-Rang Lee, Seung-Yong Eom, Ye-Seo Jin, Seong-IK Seo, Eun-SurkYi
3) 초록 :
With the growing elderly population, sarcopenia has become a critical public health issue, as it leads to decreased physical function and an increased risk of falls, ultimately hindering independent living among older adults. This study aimed to identify the correlations between sensory balance ability and general characteristics according to the presence of sarcopenia in individuals aged 65 years and older, in order to contribute to fall prevention and promote independence in daily activities. Data from 178 participants were obtained from the ongoing project “Longitudinal Study on Daily Life of Older Adults through Smart Home Implementation” conducted at ○○ University. The participants were classified into a low-balance group (n=80) and a control group (n=72) based on balance indicators. Variables were analyzed across three domains: general characteristics, physical characteristics, and sensory balance ability. General characteristics included sex, age, marital status, family composition, economic status, occupation, religion, income level, living environment, and presence of chronic diseases. Physical characteristics included BMI, SMI, FFMI, lower limb strength, maximal grip strength, TUG, STS, and SPPB, which were used to assess overall physical performance. Sensory balance ability was evaluated using the FRA_SENS comprehensive score. General characteristics were collected through a structured questionnaire, and covariate data were utilized to analyze the relationships among major variables. Physical variables were measured using the InBody 970S and HUMAC NORM Isokinetic Extremity System, while sensory balance ability was assessed with the InBody FRA 510S. Independent t-tests and chi-square tests were conducted according to variable type to compare group differences. The results showed that sensory balance composite scores significantly differed according to sex and the presence of chronic diseases. Males tended to have lower sensory balance scores than females, showing a statistically significant difference (p < .05). Additionally, participants with hypertension exhibited significantly lower sensory balance scores compared to those without hypertension. Furthermore, individuals with lower sensory balance ability demonstrated significantly longer average TUG times (p < .05), whereas no significant differences were observed in other variables. These findings suggest that sensory balance ability is significantly associated with physical function and may serve as an important clinical indicator for the prevention and management of sarcopenia in older adults.
- 이전글기반구축사업단 연구 포스터(2025년 한국운동재활학회ㆍ협회 추계학술대회) : 김하영 연구원 외 25.11.11
- 다음글체형분석 기술 고도화를 위한 리얼피티 도입 협의 진행 25.04.07
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.


